詳解 A2A-Agent2Agent- 協議
什麼是 A2A 協議
A2A(Agent2Agent)協議 是由 Google Cloud 推出的一個開放協議,旨在促進不同 AI 代理之間的互操作性。其主要目標是允許這些代理在動態的、多代理的生態系統中進行有效的通信和協作,無論它們是由不同的供應商構建的還是使用不同的技術框架。
A2A 的設計原則總結
A2A(Agent2Agent)協議的設計原則旨在提升代理之間的協作能力,確保靈活性、安全性和與現有系統的兼容性。以下是這些原則的綜合總結:
- 擁抱代理能力
- 允許代理在其自然、非結構化的模式下進行協作,無需共享內存、工具或上下文,從而實現真實的多代理場景。
- 基於現有標準構建
- 協議建立在廣泛接受的技術標準之上,如 HTTP、SSE 和 JSON-RPC,便於與企業現有的 IT 堆棧集成。
- 默認安全
- 設計支持企業級身份驗證和授權,確保只有經過授權的用戶和系統可以訪問代理,增強了系統的安全性。
- 支持長時間運行的任務
- 靈活支持從快速任務到複雜研究的多種場景,能夠在任務執行過程中提供實時反饋、通知和狀態更新。
- 模態無關
- 支持多種交互形式,包括文本、音頻和視頻流、form 、 iframe 等,增強了代理的交互能力和適應性。
整體看下來,協議在開放性、安全性、靈活性上考慮得比較多。這些點都是 MCP 有所不足的。和 MCP 的對比我們放在最後。先說正題——詳解 A2A
A2A 的參與者
A2A 協議有三個參與者:
-
用戶(User):使用代理系統完成任務的用戶(人類或服務)
-
客戶端(Client):代表用戶向不透明代理(服務、代理、應用程序)請求操作的實體。
-
服務端(Server):不透明(黑盒)的遠程代理,即 A2A 服務器。
參考如下的圖
通過上面的圖,我們可以清晰地看到三個參與者的位置,對比之前 MCP 參與者,缺少一個 Host 的參與者。這個是設計思路上的不同,是要開放實現,還是規範一個機制,在 A2A 的實現中,安全等因素,已經通過別的方式實現,但確實 User 如何發現需要的 Agent,是一個遺留的問題。
A2A 核心概念
AgentCard
AgentCard 是一個 JSON 文件,描述了 Agent 提供了什麼樣的功能,官方建議託管在 https:// base url /.well-known/agent.json。
這樣就可以直接通過 HTTP GET 獲取 AgentCard,得到有關 Agent 的描述。
一個自然的引申是:需要註冊表,無論是公開的、還是隱私的。這樣方便查找 Agent 。
但另一個方面,註冊表也可以是去中心化的。我們想象這樣一個場景:每一個網站都有一個 https:// base url /.well-known/agent.json,描述了自己可以做什麼,然後在一個 P2P 的網絡中,不斷的廣播自己的 AgentCard ——甚至這些 AgentCard,可以放在 IPFS 、或者以太坊上,這樣 Agent 的協作關係,就構成了一個自組織的 Agent 網絡。
回到 A2A,一個 AgentCard 的定義如下:
// An AgentCard conveys key information:
// - Overall details (version, name, description, uses)
// - Skills: A set of capabilities the agent can perform
// - Default modalities/content types supported by the agent.
// - Authentication requirements
interface AgentCard {
// Human readable name of the agent.
// (e.g. "Recipe Agent")
name: string;
// A human-readable description of the agent. Used to assist users and
// other agents in understanding what the agent can do.
// (e.g. "Agent that helps users with recipes and cooking.")
description: string;
// A URL to the address the agent is hosted at.
url: string;
// The service provider of the agent
provider?: {
organization: string;
url: string;
};
// The version of the agent - format is up to the provider. (e.g. "1.0.0")
version: string;
// A URL to documentation for the agent.
documentationUrl?: string;
// Optional capabilities supported by the agent.
capabilities: {
streaming?: boolean; // true if the agent supports SSE
pushNotifications?: boolean; // true if the agent can notify updates to client
stateTransitionHistory?: boolean; //true if the agent exposes status change history for tasks
};
// Authentication requirements for the agent.
// Intended to match OpenAPI authentication structure.
authentication: {
schemes: string[]; // e.g. Basic, Bearer
credentials?: string; //credentials a client should use for private cards
};
// The set of interaction modes that the agent
// supports across all skills. This can be overridden per-skill.
defaultInputModes: string[]; // supported mime types for input
defaultOutputModes: string[]; // supported mime types for output
// Skills are a unit of capability that an agent can perform.
skills: {
id: string; // unique identifier for the agent's skill
name: string; //human readable name of the skill
// description of the skill - will be used by the client or a human
// as a hint to understand what the skill does.
description: string;
// Set of tagwords describing classes of capabilities for this specific
// skill (e.g. "cooking", "customer support", "billing")
tags: string[];
// The set of example scenarios that the skill can perform.
// Will be used by the client as a hint to understand how the skill can be
// used. (e.g. "I need a recipe for bread")
examples?: string[]; // example prompts for tasks
// The set of interaction modes that the skill supports
// (if different than the default)
inputModes?: string[]; // supported mime types for input
outputModes?: string[]; // supported mime types for output
}[];
}
內容很長,但是比較簡單,我們用下圖來表示:
完整的定義可以參考這裏:https://github.com/sing1ee/a2a-agent-coder/blob/main/src/schema.ts
Task(任務)
任務是一個有狀態的實體,允許客戶端與遠程代理協作以達成特定的結果並生成相應的輸出。在任務內,客戶端與遠程代理之間會交換消息,遠程代理則生成工件作爲結果(代理即是 Agent)。
任務始終由客戶端創建,而其狀態則由遠程代理決定。如果客戶端需要,多個任務可以歸屬於同一個會話(通過可選的 sessionId 表示)。在創建任務時,客戶端可以設置這個可選的 sessionId。
代理收到請求之後,可以採取以下幾種行動:
-
立即滿足請求
-
安排稍後執行的工作
-
拒絕請求
-
協商不同的執行方式
-
向客戶端索要更多信息
-
委派給其他代理或系統
即使在完成目標後,客戶端仍然可以請求更多信息或在同一任務的上下文中進行更改。例如,客戶端可以請求:“畫一隻兔子的圖片”,代理迴應:“< 圖片 >”,隨後客戶端又可以要求:“把它畫成紅色”。
任務不僅用於傳遞工件(結果)和消息(思考、指令等),還維護着任務的狀態及其可選的歷史記錄,包括狀態變化和消息記錄。
這些特性非常重要,尤其是同一個任務的上下文,可以進行多輪的對話,這些狀態,還有歷史記錄,都有保存,這個非常匹配現在以 Chat 形式爲主的 AI 交互。
任務的定義如下:
interface Task {
id: string; // unique identifier for the task
sessionId: string; // client-generated id for the session holding the task.
status: TaskStatus; // current status of the task
history?: Message[];
artifacts?: Artifact[]; // collection of artifacts created by the agent.
metadata?: Record<string, any>; // extension metadata
}
// TaskState and accompanying message.
interface TaskStatus {
state: TaskState;
message?: Message; //additional status updates for client
timestamp?: string; // ISO datetime value
}
// sent by server during sendSubscribe or subscribe requests
interface TaskStatusUpdateEvent {
id: string;
status: TaskStatus;
final: boolean; //indicates the end of the event stream
metadata?: Record<string, any>;
}
// sent by server during sendSubscribe or subscribe requests
interface TaskArtifactUpdateEvent {
id: string;
artifact: Artifact;
metadata?: Record<string, any>;
}
// Sent by the client to the agent to create, continue, or restart a task.
interface TaskSendParams {
id: string;
sessionId?: string; //server creates a new sessionId for new tasks if not set
message: Message;
historyLength?: number; //number of recent messages to be retrieved
// where the server should send notifications when disconnected.
pushNotification?: PushNotificationConfig;
metadata?: Record<string, any>; // extension metadata
}
type TaskState =
| "submitted"
| "working"
| "input-required"
| "completed"
| "canceled"
| "failed"
| "unknown";
Artifact(工件)
工件是代理作爲任務最終結果生成的輸出。工件具有不可變性,可以被命名,並且可以包含多個部分。通過流式響應,可以將新部分附加到現有的工件中。
一個任務可以生成多個工件。例如,當執行 “創建一個網頁” 時,可能會產生單獨的 HTML 工件和圖像工件。
不得不說 A2A 出現的時機很準確,現在 AI 的一些主要的應用的形式,在協議定義上都包括了。Artifact 就是很火的一個形式。
具體的定義:
interface Artifact {
name?: string;
description?: string;
parts: Part[];
metadata?: Record<string, any>;
index: number;
append?: boolean;
lastChunk?: boolean;
}
Message(消息)
消息是包含任何非工件內容的實體。這些內容可以包括代理的思考、用戶的上下文、指令、錯誤信息、狀態更新或元數據。
所有來自客戶端的內容均以消息的形式發送。代理通過消息來傳達狀態或提供指令,而生成的結果則以工件的形式發送。
消息可以包含多個 Part(片段),以表示不同類型的內容。例如,一個用戶請求可能包括用戶的文本描述以及多個用於上下文的文件。
定義如下:
interface Message {
role: "user" | "agent";
parts: Part[];
metadata?: Record<string, any>;
}
Part(片段)
Part 是客戶端與遠程代理之間作爲消息或工件一部分交換的完整內容。每個 Part 都有其獨特的內容類型和元數據。
以下是不同類型部分的接口定義:
文本部分(TextPart)
interface TextPart {
type: "text";
text: string;
}
文件部分(FilePart)
interface FilePart {
type: "file";
file: {
name?: string;
mimeType?: string;
// 可能的內容
// oneof {
bytes?: string; // base64 編碼的內容
uri?: string;
//}
};
}數據部分(DataPart)
interface DataPart {
type: "data";
data: Record<string, any>;
}
綜合類型
type Part = (TextPart | FilePart | DataPart) & {
metadata: Record<string, any>;
};
更多的消息的細節,參考鏈接:https://a2aprotocol.ai/blog/a2a-sample-methods-and-json-responses
通信機制與異步支持
A2A 支持以下的通信機制:
-
A2A 支持安全的推送通知機制,允許代理在不連接的情況下向客戶端發送更新。
-
客戶端和服務器可以使用標準請求 / 響應模式,也可以通過 SSE 進行流式更新。
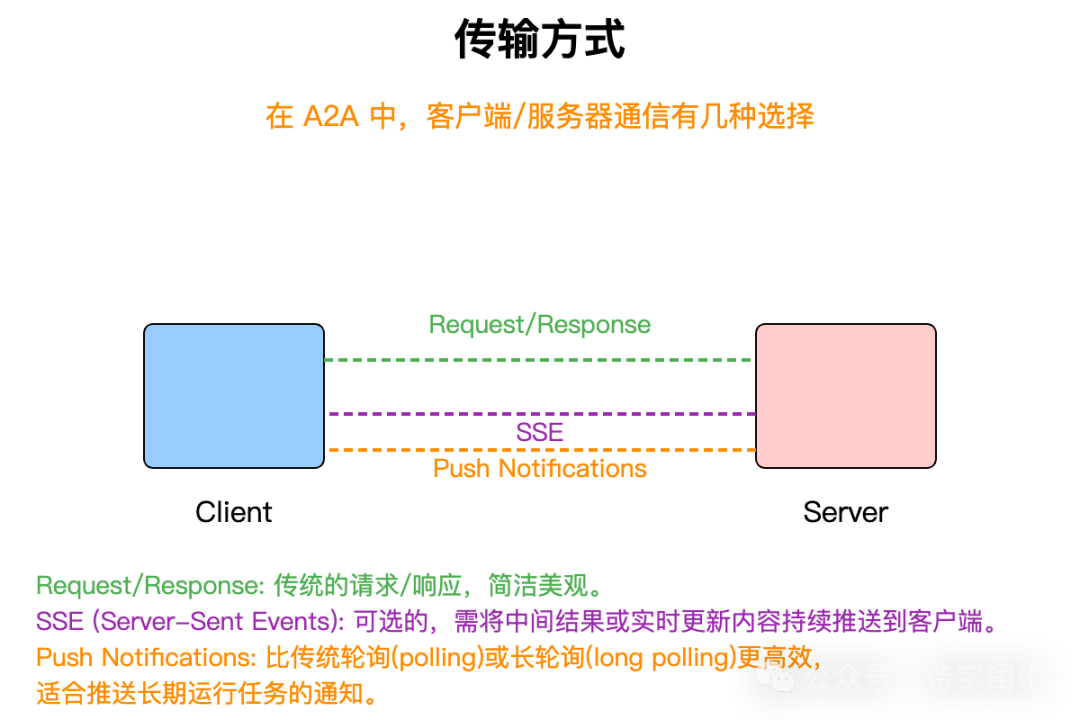在推送通知時,代理需要驗證通知服務的身份,並使用受信任的憑證進行身份驗證,以確保通知的安全性。
基於以上的通信機制,A2A 支持客戶端在處理長時間運行的任務時進行輪詢,代理也可以通過 SSE 向客戶端推送狀態更新。
這裏,最重要的是異步的支持,client 可以通過類似註冊一個 webhook,異步的獲取長時間運行任務的結果——就是 PushNotification 相關的實現。目前大家在使用 LLMs API 的時候,都會遇到一個問題,就是輸出太慢了,而且輸出的過程中,並不能做別的事情。如果有了異步的回調,或者輪詢、重新訂閱,那麼就可以在 client 的開發上,更加靈活,可以給用戶帶來更好的體驗。
以下是推送的定義:
interface PushNotificationConfig {
url: string;
token?: string; // token unique to this task/session
authentication?: {
schemes: string[];
credentials?: string;
};
}
interface TaskPushNotificationConfig {
id: string; //task id
pushNotificationConfig: PushNotificationConfig;
}
錯誤處理(Error Handling)
錯誤消息格式
以下是服務器在處理客戶端請求時遇到錯誤時響應客戶端的 ErrorMessage 格式:
interface ErrorMessage {
code: number;
message: string;
data?: any;
}
標準 JSON-RPC 錯誤代碼
以下爲服務器在錯誤場景中可以響應的標準 JSON-RPC 錯誤代碼:
動手實踐
我把官方的 ts 的示例進行了修改,支持了 OpenRouter,主要是改動了兼容 OpenAI 的 API 形式。代碼在這裏:https://github.com/sing1ee/a2a-agent-coder
我是在 Mac 環境下進行的,打開你最愛的終端:
- 安裝 Bun
brew install oven-sh/bun/bun # 針對 macOS 和 Linux- 克隆倉庫
git clone git@github.com:sing1ee/a2a-agent-coder.git- 安裝依賴
cd a2a-agent-coder
bun i- 配置環境變量
參考 .env.example 創建一個.env 文件,內容如下:
OPENAI_API_KEY=sk-or-v1-xxxxxxx
OPENAI_BASE_URL=https://openrouter.ai/api/v1
OPENAI_MODEL=anthropic/claude-3.5-haiku我用的是 OpenRouter,支付方便,模型衆多。大家嘗試的話,可以註冊一個 OpenRouter,即使沒有充值,可以有每天 50 次免費模型的額度,例如 deepseek/deepseek-chat-v3-0324:free
讓環境變量生效
export $(cat .env | xargs)- 運行 A2A Server
bun run agents:coder- 再打開一個新的終端,運行 A2A Client,這裏不需要配置 env
bun run a2a:cli以下是我之前運行的結果:
bun run a2a:cli
# result
$ bun x tsx src/cli.ts
A2A Terminal Client
Agent URL: http://localhost:41241
Attempting to fetch agent card from: http://localhost:41241/.well-known/agent.json
✓ Agent Card Found:
Name: Coder Agent
Description: An agent that generates code based on natural language instructions and streams file outputs.
Version: 0.0.1
Starting Task ID: a1a608b3-3015-4404-a83f-6ccc05083761
Enter messages, or use '/new' to start a new task.
Coder Agent > You: implement binary search
Sending...
Coder Agent [4:28:00 PM]: ⏳ Status: working
Part 1: 📝 Text: Generating code...
Coder Agent [4:28:02 PM]: ⏳ Status: working
Part 1: 📄 File: Name: src/algorithms/binary_search.py, Source: """
Implementation of the binary search algorithm in Python.
"""
def binary_search(arr, target):
"""
Performs a binary search on a sorted array to find the index of a target value.
Args:
arr (list): A sorted list of elements.
target: The value to search for in the array.
Returns:
int: The index of the target value if found, otherwise -1.
"""
low = 0
high = len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2 # Integer division to find the middle index
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid # Target found at index mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1 # Target is in the right half
else:
high = mid - 1 # Target is in the left half
return -1 # Target not found in the array
Coder Agent [4:28:02 PM]: ✅ Status: completed
SSE stream finished for method tasks/sendSubscribe.
--- End of response for this input ---
Coder Agent > You:
Exiting terminal client. Goodbye!運行過程的流程圖如下:
目前非程序員用戶想體驗,還需要耐心等待,也可以藉助 Cursor 等試一試。
A2A 與 MCP 比較
這個問題,很多人關心,我大概做了一個總結:
同時,我也在做一些思考,
-
我們要如何區分 Agent 和 Tools?真的有絕對的邊界麼?
-
目前從技術上看,A2A 適應的場景更多,包括了 MCP 的場景
-
如果未來 Agent 很多,以及 MCP server 很多,會構成一個什麼樣的網絡呢?前者更傾向於去中心化的,後者更傾向於中心化的。前者更傾向於分散自治,後者是集中的管理。
都在思考中,需要更多的實踐。
本文由 Readfog 進行 AMP 轉碼,版權歸原作者所有。
來源:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ySDTLuWvJeO9n7uBw2XxmQ